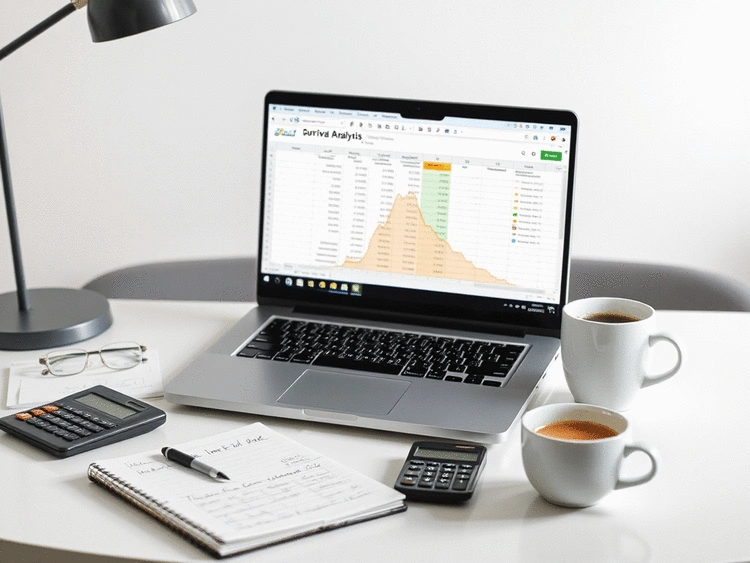
Survival Function (S(t))
Represents the probability of survival past time t.
Have you ever considered how statistical methods could transform your data analysis? Survival analysis is one such technique that allows you to uncover insights hidden in time-to-event data, making it invaluable across various fields.
Understanding the foundational elements of survival analysis is crucial for effective data interpretation. Below are the primary components and their definitions.
Represents the probability of survival past time t.
The instantaneous rate of occurrence of the event at time t.
The accumulation of hazard rates over time.
The time at which 50% of the subjects are expected to have experienced the event of interest.
Survival analysis is a powerful statistical method used to analyze the time until an event occurs, such as failure, death, or any specific event of interest. In Excel, this technique can help you uncover insights from your data, making it easier to make informed decisions. At Sheet Nerds, we believe mastering survival analysis can significantly enhance your Excel skills and boost your productivity! For more ways to leverage Excel's capabilities, check out our guide on statistical analysis in Excel.
By understanding survival analysis, you can identify trends and patterns in your data that might otherwise remain hidden. This analysis is crucial in fields such as healthcare, finance, and engineering, where decision-making often depends on time-to-event data.
So, what exactly is survival analysis? In simple terms, it's a statistical approach that evaluates the expected duration until one or more events happen. This technique is essential for predicting outcomes and managing risks efficiently. Survival analysis is particularly valued in clinical research, where it helps assess patient survival rates after treatment.
Implementing survival analysis in Excel can simplify complex calculations and allow you to visualize your results in a user-friendly manner. This accessibility is what motivates me to help you make the most of Excel, whether you're a beginner or an advanced user!
To effectively perform survival analysis, it’s essential to grasp a few key concepts, starting with survival functions and hazard rates. The survival function estimates the probability that a subject will survive beyond a certain time. Conversely, the hazard rate indicates the likelihood of the event occurring at a specific time, given that it has not yet occurred. Understanding these concepts is fundamental, much like mastering essential Excel formulas for professionals can unlock deeper data insights.
These concepts are foundational in survival analysis and will guide you as we explore more complex applications in Excel. Understanding these terms will help you to communicate your findings effectively and enhance your analytical capabilities!
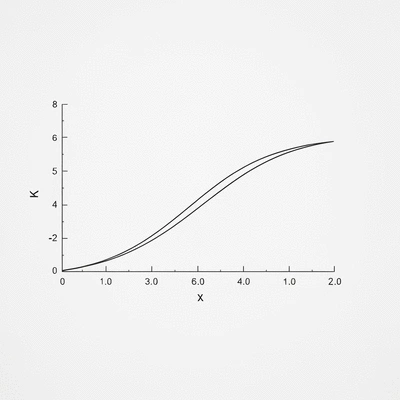
One of the most widely used methods in survival analysis is the Kaplan-Meier estimator. This non-parametric statistic estimates the survival function from lifetime data. Its visual representation, typically in the form of a step function, allows for easy interpretation of survival rates over time.
The Kaplan-Meier method is not only easy to implement in Excel but also provides clear visual insight into survival rates. As we dive deeper into this analysis, you'll learn how to create these curves, making your data storytelling more compelling!
Have you ever used survival analysis in your work or studies? What insights did you gain from it? Share your thoughts below:
Once you've created your Kaplan-Meier curves, the next critical step is interpreting and communicating your results. It's essential to present your findings in a way that is both understandable and actionable. This section will guide you through the key aspects of survival analysis interpretation, focusing on statistical assumptions, best practices for presentation, and understanding crucial metrics like confidence intervals and median survival time.
Before diving into your results, it's important to recognize the statistical assumptions underlying survival analysis. Familiarizing yourself with these assumptions helps ensure that your interpretations are sound. Here are some of the key assumptions to keep in mind:
Understanding these assumptions not only aids in validating your results but also enhances the credibility of your analysis! Be sure to review your data critically to ensure these conditions are met.
When presenting your Kaplan-Meier curves, clarity and accessibility are paramount. Here are some best practices to follow:
By following these guidelines, you'll create an engaging and informative presentation that effectively communicates your findings. Remember, the goal is to ensure your audience grasps the insights derived from your analysis. For more on making your data comprehensible, explore techniques for visualizing data in Excel.
Two essential components of survival analysis results are confidence intervals and median survival time. Understanding these elements can significantly enhance your analysis:
By mastering these concepts, you can provide a deeper understanding of your results. This understanding not only builds your confidence as an analyst but also instills trust in your audience regarding your findings!
Survival analysis is a statistical method used to analyze the time until an event of interest occurs, such as failure, death, or recovery. It's crucial for understanding durations and predicting outcomes in various fields.
Key concepts include the Survival Function (S(t)), which represents the probability of survival past time t; the Hazard Rate (λ(t)), which is the instantaneous rate of the event's occurrence at time t; and the Cumulative Hazard Function, which is the accumulation of hazard rates over time.
The Kaplan-Meier estimator is a non-parametric statistic used to estimate the survival function from lifetime data. It's widely used in clinical trials, engineering, and social sciences, often represented visually as a step function.
Important assumptions include independence of observations, that censored observations do not systematically differ from uncensored ones, and proportional hazards, meaning the hazard ratio between groups remains constant over time.
While Excel does not have built-in survival analysis functions, it can be used to perform calculations for Kaplan-Meier curves and visualize results, simplifying complex data interpretation and presentation.
As you continue your journey in survival analysis, it’s crucial to keep expanding your knowledge and skills. Here are some resources to support your learning:
From tutorials to textbooks, the following resources can help you deepen your understanding:
Utilizing these resources will allow you to continuously improve your skills and adapt to new analytical challenges!
For those who prefer structured learning, consider taking online courses. Here are a few worthwhile platforms:
These courses can help solidify your understanding and provide hands-on experience, ensuring you're well-equipped to tackle real-world scenarios.
Are you ready to dive deeper into survival analysis? At Sheet Nerds, I’m passionate about helping you unlock the full potential of Excel for your analysis needs. Start experimenting with Kaplan-Meier curves and explore the powerful insights you can uncover today! Check out our comprehensive tutorials and templates designed to guide you through the process, and learn how to master Excel data analysis practices.
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article: